Web of Science was the first major database made available for online searching by students themselves. It launched in the U.K. back in 1990 as BIDS (Bath Information and Data Service, as it was based at Bath University.)
Despite the name, Web of Science (WoS) contains something for everybody. It includes the Science, Social Science, and Arts and Humanities Citation Indexes. Clearly it cannot cover everything in such wide areas: in fact, it only covers about 5% of the journals published. However, it covers the core titles, the journals which are most cited in each field each year.
This makes it an excellent first choice for exploring a subject. You get to see what has appeared in the core journals, without anything that will be too obscure or hard to find. For undergraduate work that will usually be ideal. Researchers have the further option to search for papers which cite the key papers on their topic, to see how the field has progressed.
The latest WoS interface has a black banner with orange lettering, very like the new RHUL style. Perhaps we were ahead of a trend? Beneath it the search form has been reduced to a single search bar, like Google’s (and LibrarySearch). For more complex searches you can click “Add another field”.
It is still possible to narrow your search to just some of the indexes, to save time and reduce unwanted results. Just click on “More settings” to see the indexes and deselect those that are not needed by unchecking their boxes, as in this example:
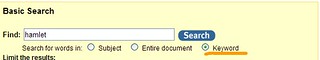
In the search above, the inverted commas around “honey bees” specify that we only want those two words together as a phrase. The asterisk after disease* is a “wild card” which will also search for ‘diseases’ or ‘diseased’.
Notice in the black banner that we are searching “Web of Science core collection” but there is an orange arrow by it. Clicking that gives the option to search other databases, in particular Biosis Previews, which lets you search the largest single life science database from 1969 to 2008. You can also choose “All databases” to search them all at the same time. This makes WoS the core resource for biologists.
When the results appear, the FindIt@RHUL lozenge which previously appeared under every result has disappeared. Don’t worry, just click on the solid block labelled “Full Text” and the familiar blue button will reappear.
The range of saving buttons above the search list has been replaced by a single block labelled “Save to EndNote online”. But it has a down arrow beside it. Click that, and you will get more options, including “Save to EndNote desktop” and “Save to RefWorks”, the main supported options at Royal Holloway.
If you liked the old interface, don’t be put off by the solid blocks of the new one, everything still works as it did. Whether you are researching for a first year essay or a doctoral thesis, WoS is a good place to start.
Adrian Machiraju